“A set is a gathering together into a whole of definite, distinct objects of our perception and of our thought - which are called elements of the set.”
Georg Cantor, German mathematician and founder of set theory
or in plain english
“A set is a well defined collection of objects”
A set in mathematics
A null set
Sets in python3
Set is a standard data type in python just like list and tuple. However, it is different from list and tuple in the the following aspects:
- A set can NOT hold multiple occurrence of same element
- The elements in a set are UNORDERED
- All the elements in a set are IMMUTABLE
Advantages
- Remove the multiple occurrence of elements from lists and tuples
- Perform mathematical operations such as intersection, union etc.
Set Initialisation
Create an empty set
vacantSet = set()
Create a set with value
Pass a list of values to set
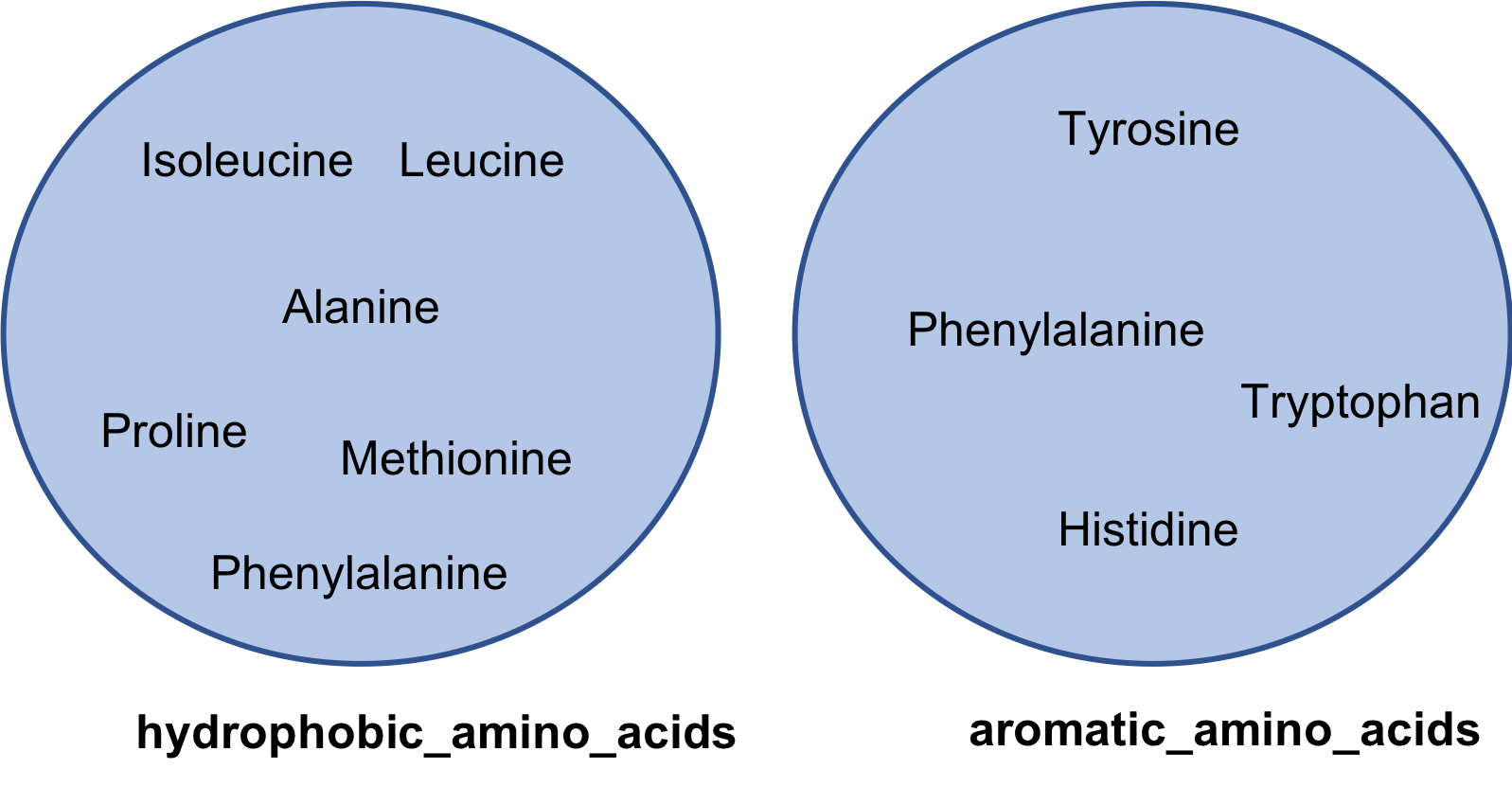
hydrophobic_amino_acids = set([ 'Isoleucine', 'Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine',
'Proline', 'Glycine' ])
aromatic_amino_acids = set(['Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan'])
hydrophobic_amino_acids
{'Alanine',
'Glycine',
'Isoleucine',
'Leucine',
'Methionine',
'Phenylalanine',
'Proline',
'Valine'}
aromatic_amino_acids
{'Histidine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Tryptophan', 'Tyrosine'}
Notice the curly braces
A set can also be initialized with curly braces {}
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine', 'Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline',
'Glycine' }
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
Curly braces can only be used to initialize a non empty set.
vacantSet = set() # its a set
vacantDict = {} # see the difference
Second example creates an empty dictionary, NOT an empty set
Add Values to the set
add method
Adds a new element to a set
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine', 'Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline',
'Glycine' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.add('Valine')
hydrophobic_amino_acids
{'Alanine','Glycine','Isoleucine',
'Leucine','Methionine','Phenylalanine',
'Proline','Valine'}
Only an immutable object can be added to a set. E.g. a string or a tuple. You will get a TypeError if you try to add a list to a set.
Remove Values from a set
remove method
Removes an element from a set
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine', 'Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline',
'Glycine' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.remove('Valine')
hydrophobic_amino_acids
{'Alanine',
'Glycine',
'Isoleucine',
'Leucine',
'Methionine',
'Phenylalanine',
'Proline'}
Disadvantage of
remove: you get a keyError if you try to remove a value that does not exist in the set
hydrophobic_amino_acids.remove('Valine')
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
KeyError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-18-d91ad6f2736b> in <module>
----> 1 hydrophobic_amino_acids.remove('Valine')
KeyError: 'Valine'
discard method
Removes a specific element from a set if it exists. Does not raise an exception if it does not exist. Exits quitely.
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine', 'Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline',
'Glycine' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.discard('Glycine')
hydrophobic_amino_acids
{'Alanine', 'Isoleucine', 'Leucine', 'Methionine',
'Phenylalanine', 'Proline'}
hydrophobic_amino_acids.discard('Glycine')
No error
pop method
Returns an arbitrary value and removes it from the set
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine','Alanine',
'Phenylalanine', 'Proline' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.pop()
‘Alanine’
hydrophobic_amino_acids
{‘Isoleucine’, ‘Phenylalanine’, ‘Proline’}
It also raises a keyError if you try to use pop on an empty set
Remove all values
clear method
Empties a set
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
aromatic_amino_acids
{‘Histidine’, ‘Phenylalanine’, ‘Tryptophan’, ‘Tyrosine’}
aromatic_amino_acids.clear()
aromatic_amino_acids
set()
Iterate over a set
Just like other collections in python, a set can be iterated over
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
for residue in aromatic_amino_acids:
print (residue)
Tyrosine Tryptophan Histidine Phenylalanine
Notice no order in the output
Sorting a set
sorted can be used to sort the members of a set. The result is a list.
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
aromatic_amino_acids_sorted = sorted (aromatic_amino_acids
)
aromatic_amino_acids_sorted
[‘Histidine’, ‘Phenylalanine’, ‘Tryptophan’, ‘Tyrosine’]
The output is a list and not a set
Remove Duplicates
If you need to remove duplicates items from a list, passed it to a set.
list_with_duplicates = ['Ala','Gly','Val','Trp','Ala']
list_with_duplicates
[‘Ala’, ‘Gly’, ‘Val’, ‘Trp’, ‘Ala’]
list_without_duplicates = set(list_with_duplicates)
list_without_duplicates
{‘Ala’, ‘Gly’, ‘Trp’, ‘Val’}
Set Operations
Python sets are very useful in computing mathematical operations such as union, intersection, difference and symmetrical difference.
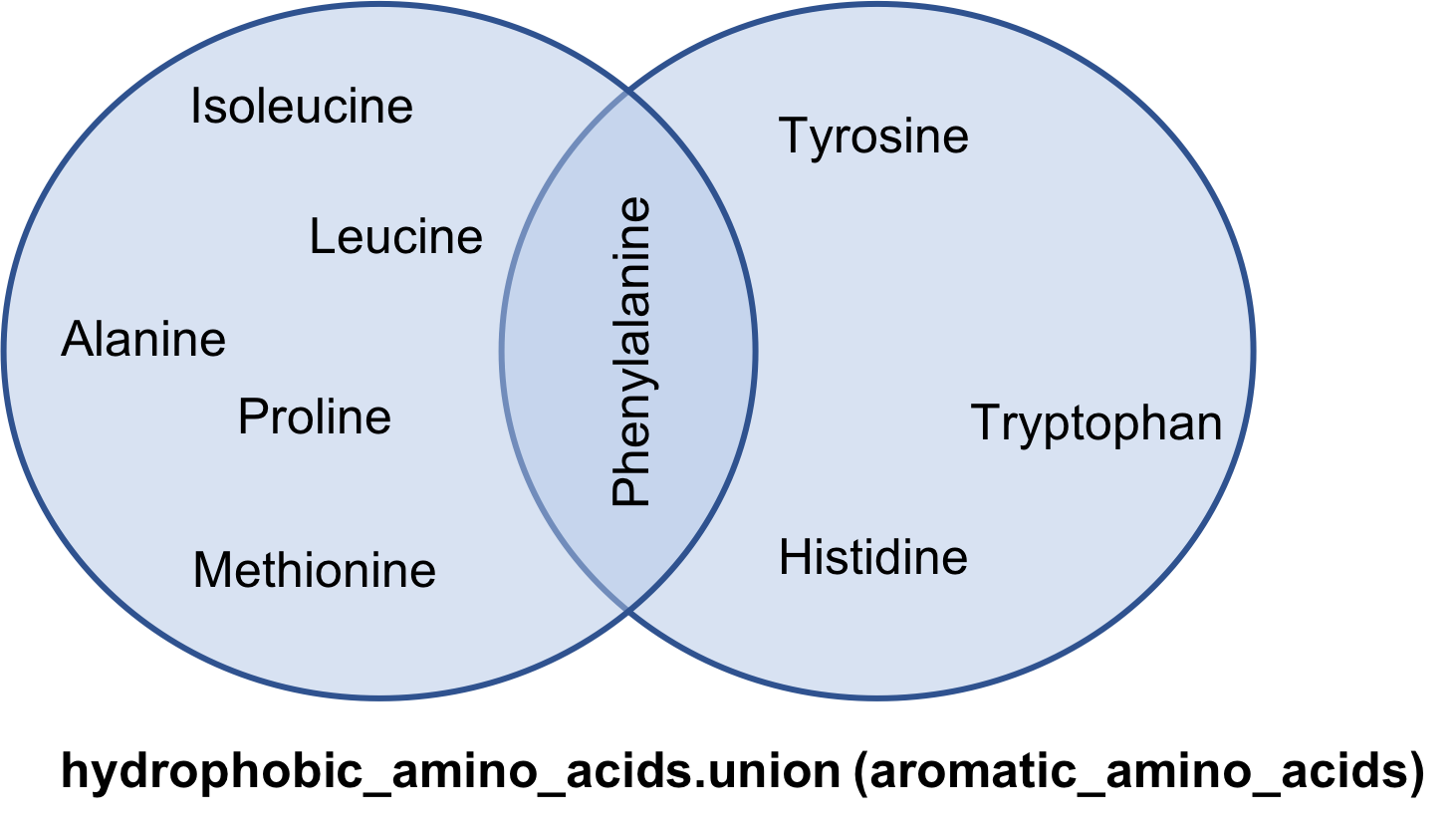
The union method
hydrophobic_amino_acids={'Isoleucine','Leucine','Alanine',
'Methionine','Phenylalanine','Proline','Glycine' }
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.union(aromatic_amino_acids)
{'Alanine',
'Glycine',
'Histidine',
'Isoleucine',
'Leucine',
'Methionine',
'Phenylalanine',
'Proline',
'Tryptophan',
'Tyrosine'}
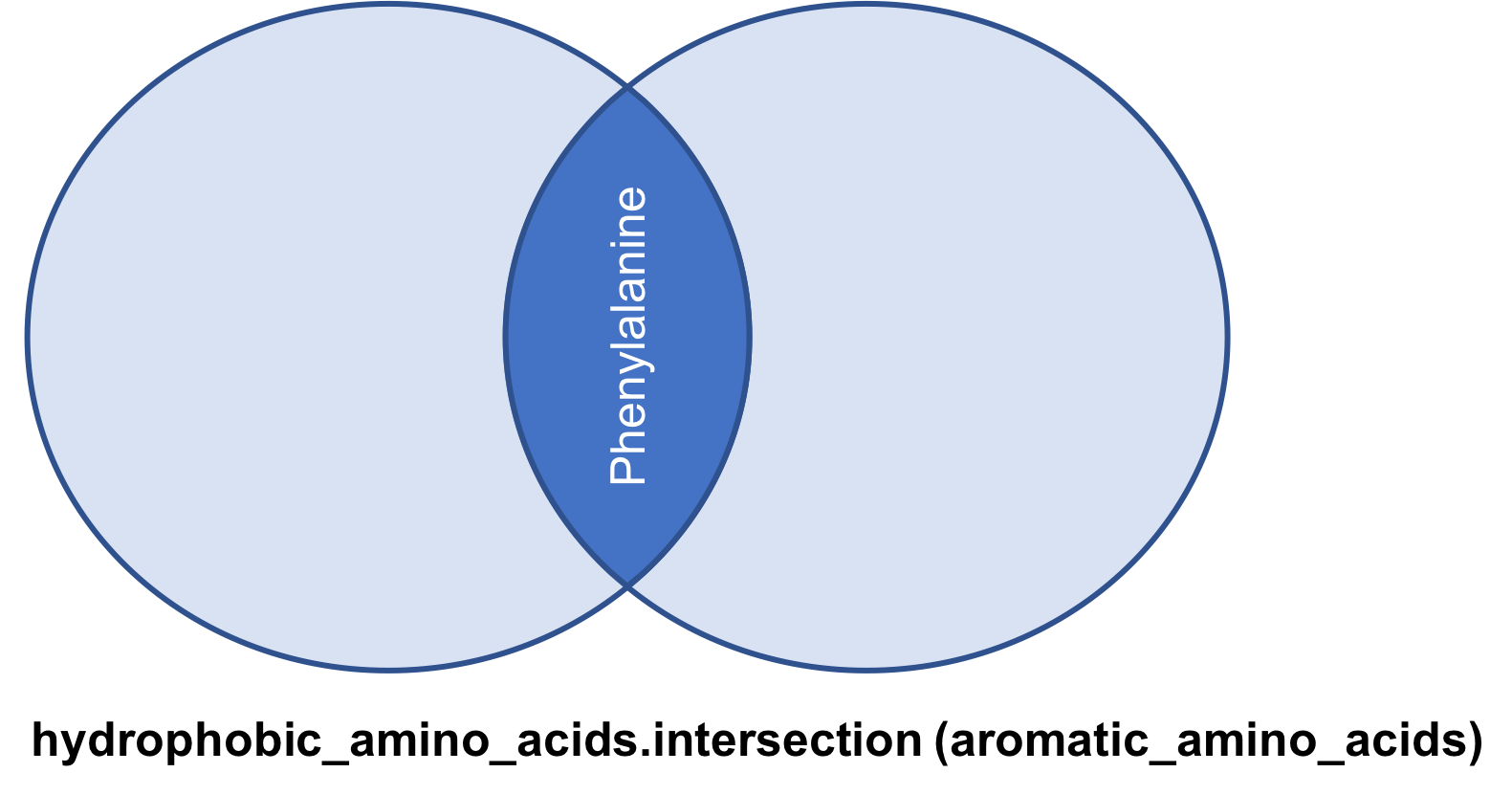
The intersection method
Returns a set that contains members that are part of both the set
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine','Leucine','Alanine',
'Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline', 'Glycine' }
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.intersection(aromatic_amino_acids
)
{‘Phenylalanine’}

isdisjoint
Checks if two sets have members in common
hydrophobic_amino_acids.isdisjoint(aromatic_amino_acids)
False
Falsebecause ‘phenylalanine’ is common member so they are notdisjoint
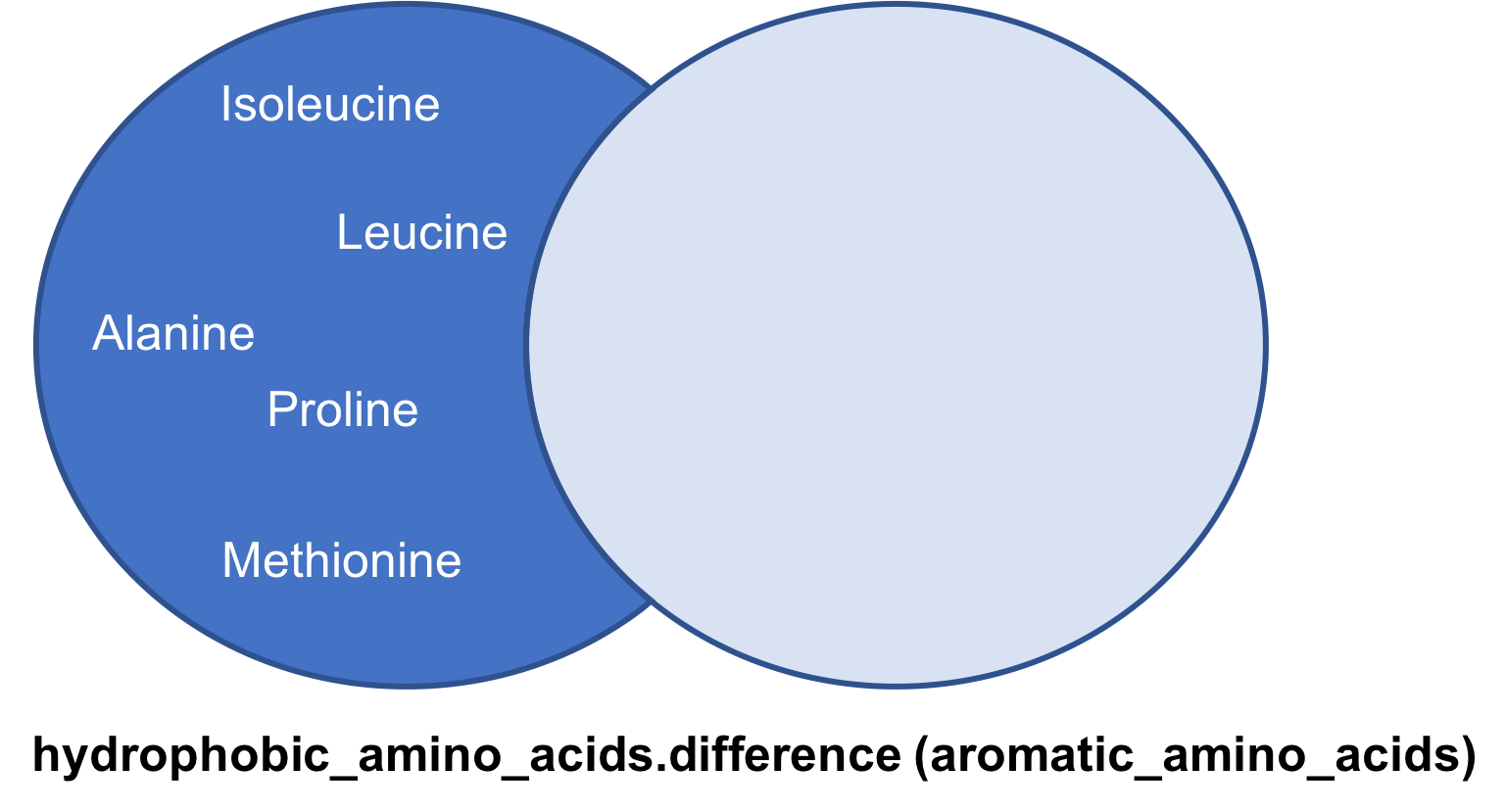
difference method
A difference of two sets A and B is a set of all members of A that are not a part of set B
hydrophobic_amino_acids={'Isoleucine','Leucine','Alanine',
'Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline', 'Glycine' }
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.difference(aromatic_amino_acids)
{‘Alanine’, ‘Glycine’, ‘Isoleucine’, ‘Leucine’, ‘Methionine’, ‘Proline’}

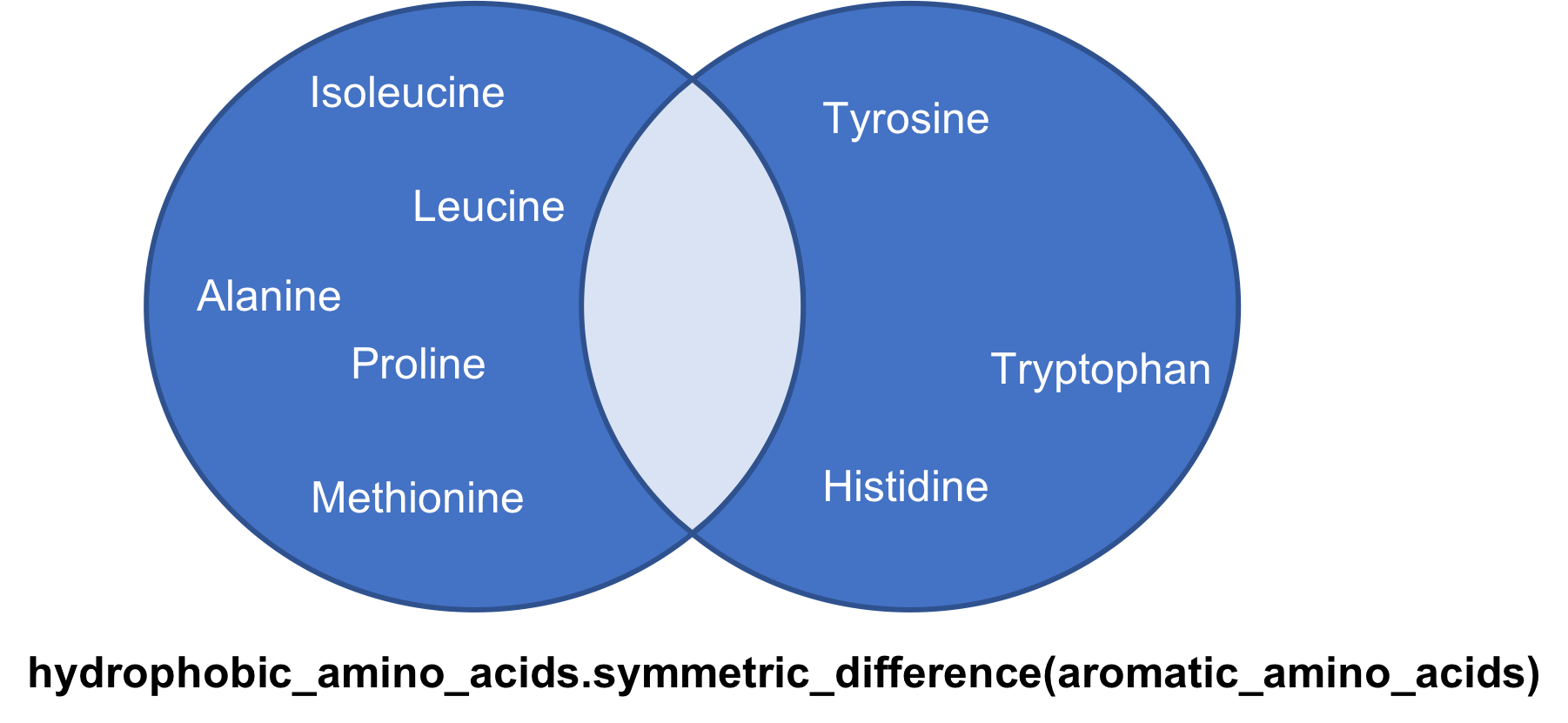
The symmetric_difference method
A symmetric difference of two sets A and B is a set whose members are a member of A or B but not both A and B
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine','Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline',
'Glycine' }
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
hydrophobic_amino_acids.symmetric_difference(
aromatic_amino_acids)
{‘Alanine’, ‘Glycine’, ‘Histidine’, ‘Isoleucine’, ‘Leucine’, ‘Methionine’, ‘Proline’, ‘Tryptophan’, ‘Tyrosine’}
Notice no ‘Phenylalanine’ which is common to both sets
hydrophobic_amino_acidsandaromatic_amino_acids

Membership tests for sets
in
In the same way a membership test is done for list and tuple, in operator can be used to test the membership of an element to a set
hydrophobic_amino_acids = { 'Isoleucine','Leucine',
'Alanine','Methionine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Proline',
'Glycine' }
'Leucine' in hydrophobic_amino_acids
True
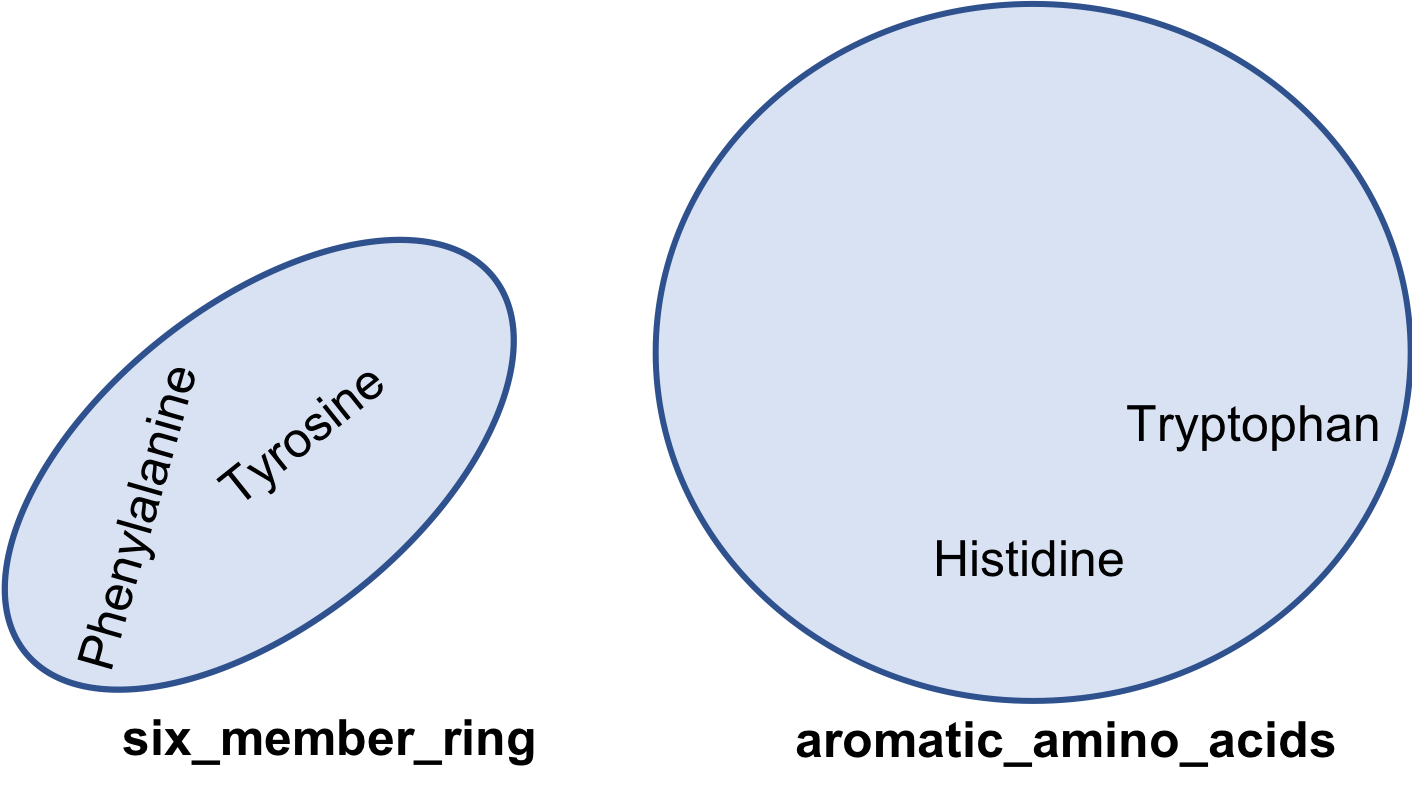
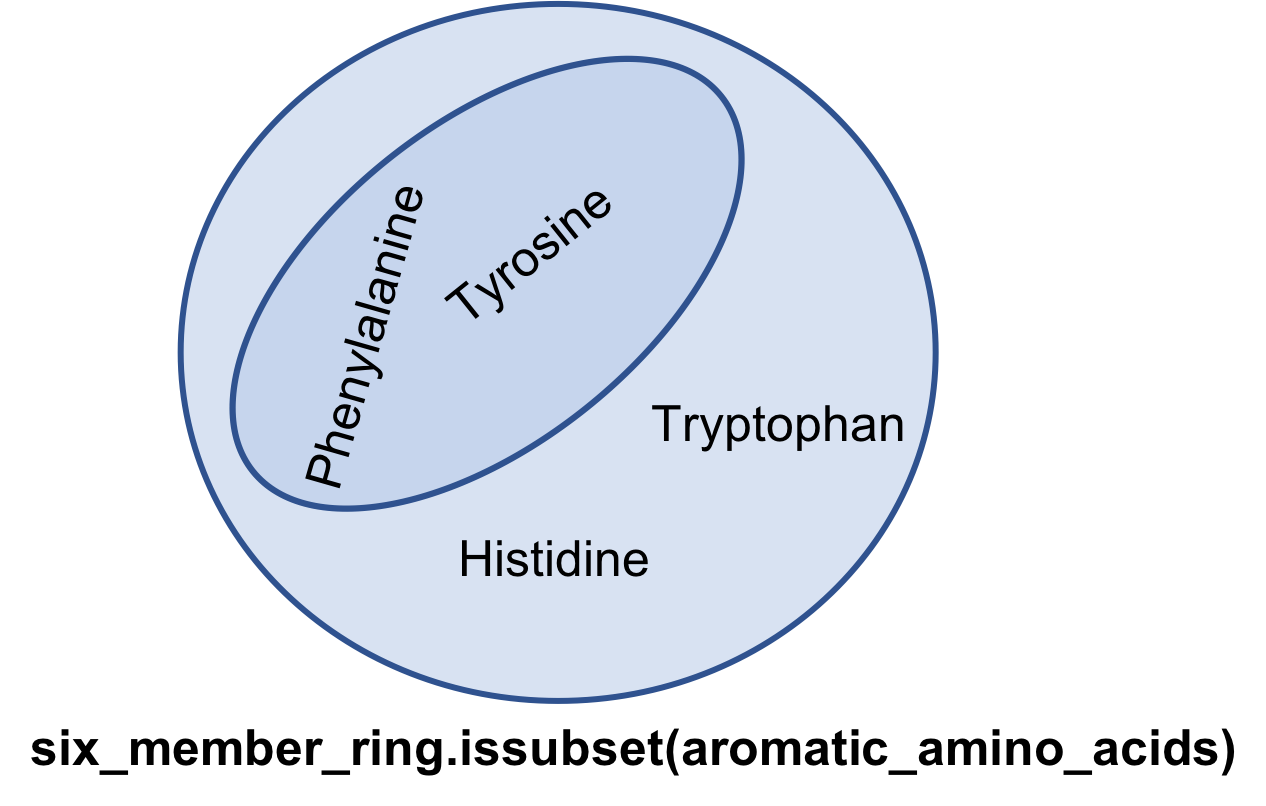
issubset
If every member of set A is only a member of set B, then set A is said to be subset of set B
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
six_member_ring = {'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine'}
six_member_ring.issubset(aromatic_amino_acids)
True
The copy method
Creates a returns a shallow copy of the set
aromatic_amino_acids = { 'Phenylalanine', 'Tyrosine',
'Histidine', 'Tryptophan' }
copy_set = aromatic_amino_acids.copy()
aromatic_amino_acids.pop()
‘Tryptophan’
aromatic_amino_acids
{‘Histidine’, ‘Phenylalanine’, ‘Tyrosine’}
copy_set
{'Histidine', 'Phenylalanine', 'Tryptophan', 'Tyrosine'}
aromatic_amino_acids has shrunken in size whereas its copy
copydoes not
The Frozensets
In python, we can have “list of lists” and “tuple of tuple”
list_of_lists = [ [0,1], [2,3],[4,5] ]
list_of_lists
[ [0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5] ]
tuple_of_tuples = ((0,1),(2,3),(4,5))
tuple_of_tuples
( (0, 1), (2, 3), (4, 5) )
But we can NOT have a set of sets
set_of_sets = { {0,1},{2,3},{4,5}}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-51-704e3c8c2290> in <module>
----> 1 set_of_sets = { {0,1},{2,3},{4,5}}
TypeError: unhashable type: 'set'
Its because sets can NOT have a mutable element, including set ifself
This is a situation where frozenset could be used
frozenset is a immutable set
immutable_set = frozenset()
immutable_set
frozenset()
A set of sets can be created if its elements are of frozenset type, and hence immutable
set_of_sets = set([frozenset(), frozenset()])
set_of_sets
{frozenset()}
The End